Final Rangkuman
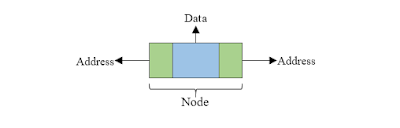
Name: Anthony Christoper NIM: 2301911590 Class: CB01 DOSEN: Ferdinand Ariandy Luwinda (D45222) & Hentry Chong(D4460) Data Structure : Doubly Linked List Doubly linked list is a collection of nodes linked together in a sequential way. Each node of the list contains two parts data part and reference/address part. The basic structure of node is shown in the below image: Doubly linked list is almost similar to singly linked list except it contains two address or reference fields, where one of the address field contains reference of the next node and other contains reference of the previous node. First and last node of linked list contains a terminator generally a NULL value, that determines the start and end of the list. Doubly linked list is sometimes also referred as bi-directional list since it allows traversal of nodes in both direction. The basic structure of a doubly linked list is represented as: Since doubly linked list allows the traversal of nodes in...



