Final Rangkuman
Name: Anthony Christoper
NIM: 2301911590
Class: CB01
DOSEN: Ferdinand Ariandy Luwinda (D45222) & Hentry Chong(D4460)
Data Structure : Doubly Linked List
Doubly linked list is a collection of nodes linked together in a sequential way. Each node of the list contains two parts data part and reference/address part. The basic structure of node is shown in the below image:
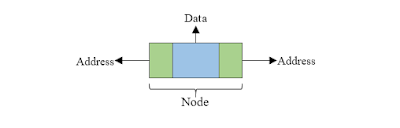
Doubly linked list is almost similar to singly linked list except it contains two address or reference fields, where one of the address field contains reference of the next node and other contains reference of the previous node. First and last node of linked list contains a terminator generally a NULL value, that determines the start and end of the list. Doubly linked list is sometimes also referred as bi-directional list since it allows traversal of nodes in both direction. The basic structure of a doubly linked list is represented as:

Since doubly linked list allows the traversal of nodes in both direction hence we can keep track of both first and last nodes.
The implementation of doubly linked list in C programming language :
struct node {
int data; // Data field
struct node *prev; //Address previous node
struct node *next; //Address next node
};
Data Structure: Circular Linked List
A circular linked list is basically a linear list that may singly or doubly. The only difference between doubly linked list is that there is no any NULL value to terminating the list. in fact in the list every node points to the next node and last node points to the first node, thus forming a circle.Since it forms a circle with no end stop hence it called as circular linked list.
To make it happen we need to know where our address is first before we start making push insertion. The push insertion will be pushing from the front(beginning) and make a pop will be delete address.
struct node{
int data; // value
struct node *next, *prev; // address
}*head,*curr,*tail;
void push(int a)
{
curr = (struct Data*)malloc(sizeof(struct Data));//create address
curr->value = a;//insert value input a
if(head==NULL){// if head don have any address then we create one
head = tail = curr;
}
else{
tail->next = curr;// move tail to curr
curr->prev = tail;// move curr to tail
tail = curr;// then we have tail and curr swap position
}
head->prev = tail->next = NULL;// if we create something like 10->20->NULL->40 it will print output of 10->20->0->40
}

void pop()// delete from front to behind
{
curr = head;// start the curr from the head
if(tail == head){
free(curr);
tail = head = curr = NULL;// if tail and head pointing same address it will be deleted
}
else
{
while(curr->next!=tail){
curr = curr->next;// walk until finding the last input
}
free(tail); // delete value and memory
tail = curr;// the curr last position become the tail position
tail->next = NULL;// the delete value get null input
}
}

source:
https://codeforwin.org/2015/10/doubly-linked-list-data-structure-in-c.html
https://codeforwin.org/2015/11/circular-linked-list-data-structure.html
https://codeforwin.org/2015/11/c-program-to-insert-node-in-circular-linked-list.html
What is Hashing?
Hashing is the process of mapping large amount of data item to smaller table with the help of hashing function.
Hashing is also known as Hashing Algorithm or Message Digest Function.
It is a technique to convert a range of key values into a range of indexes of an array.
It is used to facilitate the next level searching method when compared with the linear or binary search.

BNS is also known as versions of sorted version of binary tree
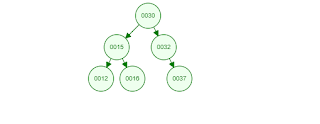
source:
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BST.html
AVL TREE is pretty similar to binary search tree but AVL can adjust the balance of the tree automatically
The root of the node AVL tree is 0
The leaf of the right or leaf of the left is 1.
if the leaf is more than 1 the tree will automatically adjust the balance

The above picture is from the right node input and will be rotating to the left.

and this other picture is node from the left side and the rotation will be going to the right.

the correct solution of the wrong AVL tree is below:-

here another example :-

Example of Single rotation

below example of Doubly rotation

AVL Tree Source:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/avl_tree_algorithm.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:AVL_Tree_Example.gif
AVL TREE PPT binus
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/AVLtree.html
RED Black Tree
RBT(Red Black Tree) juga salah satu binary tree tapi dengan susun property merah dan hitam
What is the Codition of Red-Black Tree Insertion?

{
curr = (struct Data*)malloc(sizeof(struct Data));//create address
curr->value = a;//insert value input a
if(head==NULL){// if head don have any address then we create one
head = tail = curr;
}
else{
tail->next = curr;// move tail to curr
curr->prev = tail;// move curr to tail
tail = curr;// then we have tail and curr swap position
}
head->prev = tail->next = NULL;// if we create something like 10->20->NULL->40 it will print output of 10->20->0->40
}

void pop()// delete from front to behind
{
curr = head;// start the curr from the head
if(tail == head){
free(curr);
tail = head = curr = NULL;// if tail and head pointing same address it will be deleted
}
else
{
while(curr->next!=tail){
curr = curr->next;// walk until finding the last input
}
free(tail); // delete value and memory
tail = curr;// the curr last position become the tail position
tail->next = NULL;// the delete value get null input
}
}

source:
https://codeforwin.org/2015/10/doubly-linked-list-data-structure-in-c.html
https://codeforwin.org/2015/11/circular-linked-list-data-structure.html
https://codeforwin.org/2015/11/c-program-to-insert-node-in-circular-linked-list.html
What is Hashing?
Hashing is the process of mapping large amount of data item to smaller table with the help of hashing function.
Hashing is also known as Hashing Algorithm or Message Digest Function.
It is a technique to convert a range of key values into a range of indexes of an array.
It is used to facilitate the next level searching method when compared with the linear or binary search.

BNS is also known as versions of sorted version of binary tree
for the node of the left subtree is contain smaller number than those store in x
for the node of the right subtree is contain greater number than those store in x
there are three operation in BNS:
- insert()
- search()
- remove()
source:
The insert of BNS is to store is done recursively.
let the new node's key be X, then we have a number of 30 of the beginning of the first node.
if the node key input is smaller it will move the node to the left subtree side, if the node key is greater than it will move to the right subtree side.
here is the example:-
Now we will discuss search of BNS or can be call find of BNS. The search is pretty easy it just finds the node key of the X in the tree. if the search found the node it search then it will print the "the node key is found in the tree". The search algorithm is pretty much similar to insert but it job not to insert but to find only.
Lastly, remove BNS which is to remove the node of the tree. just as previous picture if I want to remove the node 35 the 32 will be taking over it.
here the example :

source:
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BST.html
AVL TREE is pretty similar to binary search tree but AVL can adjust the balance of the tree automatically
The root of the node AVL tree is 0
The leaf of the right or leaf of the left is 1.
if the leaf is more than 1 the tree will automatically adjust the balance

The above picture is from the right node input and will be rotating to the left.

and this other picture is node from the left side and the rotation will be going to the right.

the correct solution of the wrong AVL tree is below:-

here another example :-

Example of Single rotation

below example of Doubly rotation

AVL Tree Source:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/data_structures_algorithms/avl_tree_algorithm.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:AVL_Tree_Example.gif
AVL TREE PPT binus
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/AVLtree.html
RED Black Tree
RBT(Red Black Tree) juga salah satu binary tree tapi dengan susun property merah dan hitam
What is the Codition of Red-Black Tree Insertion?



Comments
Post a Comment