Today Topic
Data Structure : Doubly Linked List
Doubly linked list is a collection of nodes linked together in a sequential way. Each node of the list contains two parts data part and reference/address part. The basic structure of node is shown in the below image:
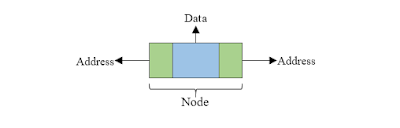
Doubly linked list is almost similar to singly linked list except it contains two address or reference fields, where one of the address field contains reference of the next node and other contains reference of the previous node. First and last node of linked list contains a terminator generally a NULL value, that determines the start and end of the list. Doubly linked list is sometimes also referred as bi-directional list since it allows traversal of nodes in both direction. The basic structure of a doubly linked list is represented as:

Since doubly linked list allows the traversal of nodes in both direction hence we can keep track of both first and last nodes.
The implementation of doubly linked list in C programming language :
struct node {
int data; // Data field
struct node *prev; //Address previous node
struct node *next; //Address next node
};
Data Structure: Circular Linked List
A circular linked list is basically a linear list that may singly or doubly. The only difference between doubly linked list is that there is no any NULL value to terminating the list. in fact in the list every node points to the next node and last node points to the first node, thus forming a circle.Since it forms a circle with no end stop hence it called as circular linked list.
C program to insert a new node in a circular Linked List:
//Basic structure of node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
}*head;
//Create a circular linked list of n nodes.
void(createList(int n)
{
int i, data;
struct node *prevNode, *newNode;
if(n ?= 1)
{
head = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf("Enter data of 1 node: ");
scanf("%d", &data);
head->data =data;
head->next =NULL;
prevNode = head;
//creates and links rest of the n-1 nodes
for(i = 2; i<=n; i++)
{
newNode = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
printf("Enter data of %d node: ", i);
scanf("%d", &data;
newNode->data = data;
newNode -> NULL;
prevNode->next = newNode; //Links the previous node with newly created node
prevNode = newNode; //Moves the previous node ahead
}
prevNode -> =head; //Links the last node with first node
printf("\nCIRCULAR LINKED LIST CREATED SUCCESFULLY\N);
source:
https://codeforwin.org/2015/10/doubly-linked-list-data-structure-in-c.html
https://codeforwin.org/2015/11/circular-linked-list-data-structure.html
https://codeforwin.org/2015/11/c-program-to-insert-node-in-circular-linked-list.html




Comments
Post a Comment